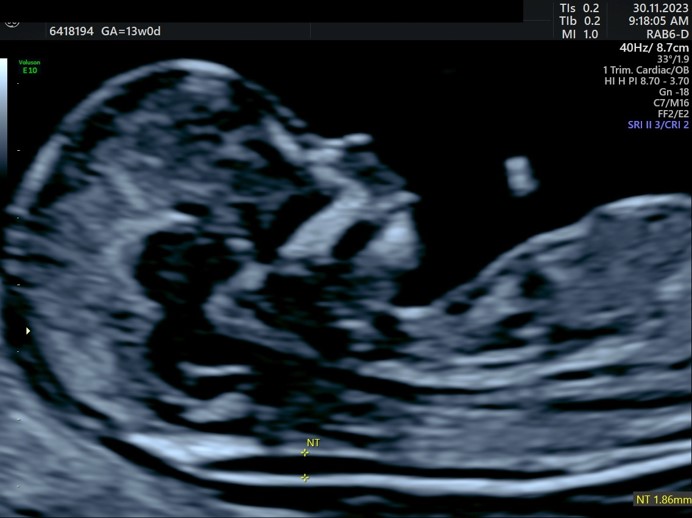
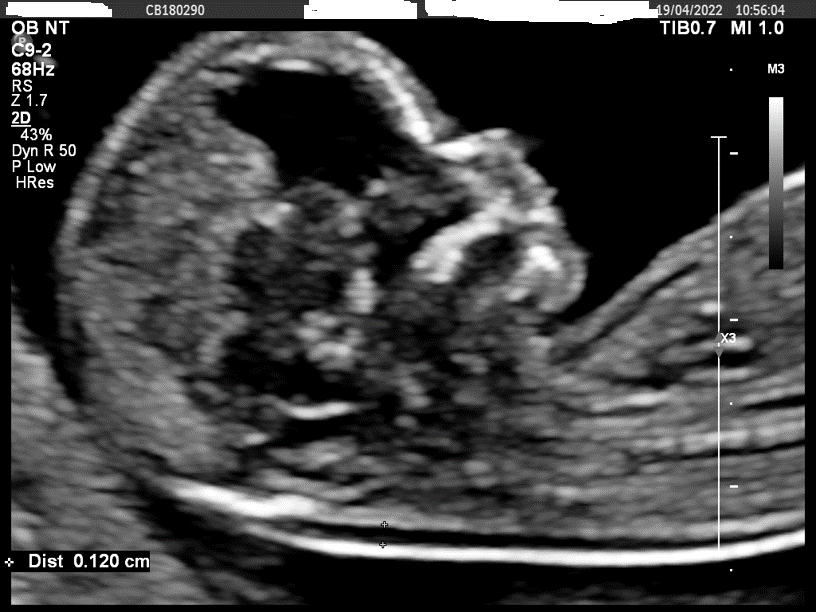
Protocols For Measuring The Nuchal Translucency
- Gestational age should be 11 to 13 weeks 6 days
- The fetal crown-rump length should be between 45 and 84mm.
- A good sagittal section of the fetus must be obtained, with the fetus horizontal on the screen.
- An ideal mid-sagittal view of the face should be obtained. This is defined by the presence of the echogenic tip of the nose and rectangular shape of the palate anteriorly, the translucent diencephalon in the centre and the nuchal membrane posteriorly.
- Minor deviations from the exact midline plane would cause non-visualisation of the tip of the nose and visibility of the infraorbital process of the maxilla.
- The fetus should be in a neutral position, with the head in line with the spine, not hyper-extended or flexed.
- When the head is hyperextended the measurement can be falsely increased
- When the head is flexed the measurement can be falsely decreased
- The fetus should be magnified so that the head and thorax occupy the whole of the image.
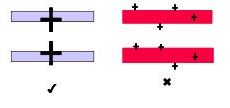
- The widest part of the nuchal translucency must be measured.
- Measurements should be taken with the inner border of the horizontal line of the calipers placed ON the line that defines the nuchal translucency thickness – the crossbar of the caliper should be such that it is hardly visible as it merges with the white line of the border, not in the nuchal fluid.
- Demonstrate the two lines of the nuchal membrane crisply from occiput to upper thorax.
- Care must be taken to distinguish between fetal skin and amnion, and to avoid compression of the nuchal membrane on the uterine wall.
During the scan more than one measurement must be taken and the maximum one that meets all the above criteria should be recorded in the database. It is good practice to retain at least one image for your patient records.
How to optimise your settings for accurate caliper placement:
- Avoid post freeze zoom.
- Reduce the depth.
- Reduce the sector width.
- Move the focus to the level of the NT.
- Reduce the gain to reduce the fuzzy edges.
- Reduce the dynamic range.
- Review use of harmonics.
Examples: